The New Georgia Encyclopedia is supported by funding from A More Perfect Union, a special initiative of the National Endowment for the Humanities.
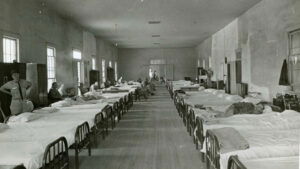
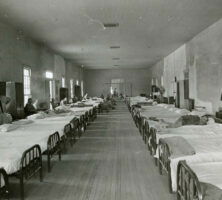
A sleeping ward at Milledgeville State Hospital for the Insane, circa 1940. Authorities at the hospital practiced compulsory sterilization of patients throughout the 1940s and 1950s. Following an award-winning 1959 report by Atlanta Constitution Jack Nelson, the number of operations dropped dramatically before finally ceasing in 1963.
Courtesy of Special Collections & Archives, Georgia State University Library, Atlanta Journal-Constitution Photographic Archive .
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to Special Collections and Archives at Georgia State University.
Francis Galton was an English statistician whose theories on heredity lead him to develop the field of eugenics. During the early twentieth century, Galton's ideas gained support among scientific and medical professionals, politicians, and Progressive-era reform groups.
Image from Eveleen Myers
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
This tinted postcard of the Georgia State Sanitarium (later Central State Hospital) depicts the grounds of the institution circa 1905. During this time the hospital was under the leadership of Theophilus O. Powell, who implemented more precise methods of diagnosis.
Courtesy of Melinda Smith Mullikin, New Georgia Encyclopedia
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A small area of concentrated vegetable production, mostly cabbage, pumpkins, tomatoes, and sweet corn, exists north of Atlanta. A cabbage farm in Fannin County is pictured.
Courtesy of Georgia Department of Economic Development.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Georgia Department of Economic Development.
Members of the board for the Nuclear Threat Initiative include, back row, left to right: Fujia Yang, Eugene E. Habiger, Hisashi Owada, Susan Eisenhower, Sam Nunn, Ted Turner, Andrei Kokoshin, Jessica Mathews, Charles B. Curtis, Prince El Hassan bin Talal. Front row, left to right: William Perry, Rolf Ekeus, Richard G. Lugar, Nafis Sadik.
Courtesy of Nuclear Threat Initiative
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Voters in Fulton County line up at the polls in the early 1970s.
Courtesy of Atlanta University Center, Robert W. Woodruff Library Archives, Voter Education Project Organizational Records.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the Atlanta University Center Robert W. Woodruff Library and Archives Research Center.
U.S. president Lyndon B. Johnson signs the Voting Rights Act into law on August 6, 1965, as a crowd, including Martin Luther King, looks on. The law prohibited racial discrimination in voting procedures. Today Georgia voters must be eighteen years of age and legal residents of a state county.
Photograph by Wikimedia
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Election day in Kingsland, Camden County, in the early 1960s, before the advent of voting booths. Georgia's elections were governed by the county unit system, which gave more weight to rural votes than to urban votes, until 1962. Even though they were home to a minority of Georgians, rural counties usually decided the winners of statewide elections.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
cam368.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
Atlanta has served as the capital city of Georgia since 1868. The current gold-domed capitol building, completed in 1889, houses the General Assembly in downtown Atlanta.
Courtesy of Georgia Info, Digital Library of Georgia.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Digital Library of Georgia.
In 1966 Lester Maddox defeated former governor Ellis Arnall in the Democratic gubernatorial primary in a major political upset. Subsequently, as a result of a close race between Maddox and Republican Bo Callaway, the General Assembly chose Maddox as governor.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Richard B. Russell Library for Political Research and Studies at the University of Georgia.
Arnall, who had served as governor from 1943 to 1947, became the front-runner in the 1966 gubernatorial race. His accomplishments as a reform governor included establishing a retirement system for teachers, repealing the state's poll tax, lowering the voting age to eighteen, and gaining reaccreditation of the University System of Georgia.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Bo Callaway was elected in 1964 as the first Republican congressman from Georgia since 1875. He ran for governor in the 1966 general election, but the presence of a write-in candidate prevented him from receiving the constitutionally required majority, costing him the election.
Image from George Augusta
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Eugene Talmadge served as governor of Georgia from 1933 to 1937 and again from 1941 to 1943. His tenure included the controversial Cocking affair in 1941, and his death in 1946 touched off the unprecedented "three governors controversy."
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Richard B. Russell Library for Political Research and Studies at the University of Georgia.
Harmon Caldwell, president of the University of Georgia during the Cocking affair in 1941, announced he would resign from his post if Walter Cocking didn't receive a hearing before termination of his position as dean of the school's College of Education.
Courtesy of Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library, University of Georgia Libraries, Georgia Photo File.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
Herman Talmadge served as governor of Georgia from 1948 to 1954. In 1956 Talmadge was elected to the U.S. Senate, where he served until his defeat in 1980.
Courtesy of Richard B. Russell Library for Political Research and Studies, University of Georgia Libraries, Ed Friend Visual Materials.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Richard B. Russell Library for Political Research and Studies at the University of Georgia.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Herman Talmadge, son of Georgia governor Eugene Talmadge, took the governor's office briefly in 1947, and again after a special election in 1948.
Courtesy of Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library, University of Georgia Libraries, Georgia Photo File.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.