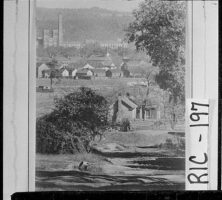The New Georgia Encyclopedia is supported by funding from A More Perfect Union, a special initiative of the National Endowment for the Humanities.
Members of a family pose on the porch of their farmhouse in Carroll County, ca. 1870-99. Kitchen gardens, such as the one in the foreground, were traditionally tended by women.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
car156.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A Dalton family poses in front of its mill house in the Chattanooga Avenue area in 1919. Textile mills in Dalton held contests to determine the most attractive yards of the mill homes, and this yard was one of the winners.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
wtf261.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Mill villages were a prevalent form of vernacular architecture in Georgia during the industrial era. King Mill appears in the background of this view of Augusta, ca. 1912 to 1915.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
ric197.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
The owners of this cabin appear in front of their home in Union Point, Greene County, ca. 1900. The timber for such cabins was usually cut and hewn on the building site.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
grn145.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
A family poses in front of its mill house, located in the Chattanooga Avenue area of Dalton, in 1919 after winning a contest sponsored by a textile mill for the most attractive yard.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #wtf260.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Singers perform during the Sapelo Island Cultural Day, held each October on the island. The festival celebrates the songs, stories, dances, and food of the Geechee and Gullah culture, which developed on the Sea Islands among enslaved West Africans between 1750 and 1865.
Photograph by Jennifer Cruse Sanders
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
First published in 1844, The Sacred Harp songbook has helped to promote the style of singing known as "Sacred Harp," "shape-note," or "fasola" singing.
Courtesy of Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A statue of Brer Rabbit, a major character in the Uncle Remus tales by Joel Chandler Harris, stands in front of the Putnam County Courthouse. Harris's work, particularly his animal tales, brought African American folklore into the public spotlight.
Image from Mdxi
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A story cloth by textile artist and Hmong refugee May Tong Moua depicts Hmong villagers fleeing Communist forces (upper right-hand corner) in Laos and crossing the Mekong River to arrive at a refugee camp in Thailand. A resident of Lilburn, May Tong Moua is among a number of Hmong refugees who resettled in DeKalb and Gwinnett counties. The story cloth, made in 1991, is housed at the Atlanta History Center.
Courtesy of Atlanta History Center.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Atlanta History Center.
Exterior view of the Hambidge Center Gallery. The gallery is one way the center provides public accessibility.
Courtesy of Explore Georgia, Photograph by Ralph Daniel.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to Explore Georgia.
Mary Hambidge founded the Jay Hambidge Art Foundation in 1934, naming it after her late partner. The foundation, later the Hambidge Center, was incorporated ten years later as a nonprofit organization for educational and scientific purposes.
Courtesy of Hambidge Center for Creative Arts and Sciences
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
An artist at work in the Hambidge Center studio.
Courtesy of Explore Georgia, Photograph by Ralph Daniel.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to Explore Georgia.
Pottery made in the "U Do Raku" workshop, which is an annual event at the Hambidge Center. Raku describes the unique process of kiln-firing the hand-thrown pottery before removing it to "reduce" in a cooler environment.
Courtesy of Hambidge Center for Creative Arts and Sciences
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Baker's Creek Mill at the Hambidge Center, where artists from around the world can apply to spend two weeks to two months in residency.
Courtesy of Explore Georgia, Photograph by Ralph Daniel.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to Explore Georgia.