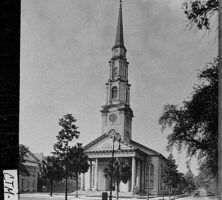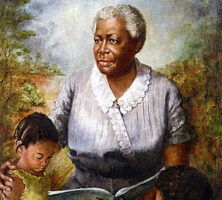The New Georgia Encyclopedia is supported by funding from A More Perfect Union, a special initiative of the National Endowment for the Humanities.
Educator and suffragist Adella Hunt Logan received an honorary master's degree from Atlanta University in 1901. The degree was "honorary" because the school was not yet accredited to grant graduate degrees.
From Adele Logan Alexander's personal collection
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Adella Hunt Logan is pictured in her wedding dress in Atlanta. She married Tuskegee Institute treasurer Warren Logan in 1888.
From Wikimedia
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
After accepting a teaching position at the Tuskegee Institute in 1883, Adella Hunt Logan forged enduring relationships with fellow educators and civil rights leaders. Among her new acquaintances was NAACP cofounder W. E. B. Du Bois, with whom she shared a lifelong correspondence.
Courtesy of Special Collections and University Archives, University of Massachusetts Amherst Libraries
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Tuskegee Institute founder Booker T. Washington and school treasurer Warren Logan are featured in the Lincoln Jubilee Album, shortly after Washington's death in 1915.
Image from Wikimedia, Lincoln Financial Foundation Collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Julia Flisch, a native of Augusta, was instrumental to the development of higher-education opportunities for women in Georgia. Over the course of her career, Flisch taught at Georgia Normal and Industrial College (later Georgia College and State University) in Milledgeville, Tubman High School for Girls in Augusta, and the Junior College of Augusta (later Augusta State University).
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Ellen Louise Axson and Woodrow Wilson were married in Savannah on June 24, 1885. Before her marriage, Axson attended the Art Students League of New York.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Ellen Axson Wilson, pictured in 1912, became the first Georgian to serve as first lady of the United States when her husband, Woodrow Wilson, won the 1912 presidential election. Ellen Wilson was born in Savannah and grew up primarily in Rome, where her father was a Presbyterian minister.
Courtesy of Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Independent Presbyterian Church in Savannah, pictured circa 1930, counted Mary Telfair, the benefactor of Telfair Museums, as a member in the nineteenth century. U.S. first lady Ellen Axson Wilson, whose paternal grandfather began serving as pastor in 1857, was born in the manse of the church in 1860 and married there in 1885.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
ctm159.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
Ellen Axson Wilson poses in 1910 with her husband, Woodrow Wilson, who served as governor of New Jersey in 1911-12. Beginning in 1905 Ellen Wilson, who studied art before her marriage, resumed painting and spent occasional summers at an art colony in Connecticut.
Courtesy of Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Woodrow Wilson and his wife, Ellen Axson Wilson (standing), pose with their three daughters in 1912, the same year that Woodrow Wilson won the presidential election. As first lady, Ellen Wilson campaigned to improve conditions on the streets of Washington, D.C., and planned the rose garden on the White House grounds.
Courtesy of Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
U.S. president Woodrow Wilson's carriage proceeds down Broad Street in Rome during the funeral of his wife, Ellen Axson Wilson, on August 11, 1914. A native of Rome, the first lady died in the White House on August 6.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, # flo128.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
Fuller Callaway Jr. attends a picnic in LaGrange with Alice Hinman Hand, whom he married in 1930, and his mother, Ida Callaway. Like his father, Fuller Callaway Jr. was heavily involved in the textiles industry.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
trp257.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
The award-winning Callaway Gardens in Pine Mountain boasts 14,000 acres of gardens, a nature preserve, and a family-oriented resort including restaurants, shopping, and nature exhibits. Guests to the gardens enjoy hiking, golf, racquet sports, fly-fishing, and range shooting.
Image from JR P
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The self-made businessman Fuller E. Callaway displayed an entrepreneurial spirit at a young age. The son of a minister, Callaway grew up to become a successful manufacturer and banker with diverse commercial interests and a reputation for generosity and moral leadership.
Courtesy of Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Unity Mills was the second mill in which Fuller Callaway invested, and the LaGrange plant shipped its first finished cotton product on December 24, 1901. Callaway served as secretary-treasurer of Unity.
Courtesy of Troup County Archives, LaGrange, Callaway Educational Association Photo Collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Callaway Mills employees sampling cotton to determine its grade and, therefore, its price in 1926.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #trp190.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
The home of Cason Callaway, a prominent textile manufacturer, at his Blue Springs Farms in Harris County is pictured in 1933. Following his retirement in 1938, Callaway established an experimental farm of 40,000 acres on this property.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, # trp168.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
Cason Jewell Callaway was a successful businessman and state agricultural leader during the first half of the twentieth century. He founded Callaway Gardens, in Harris County, in 1952.
Courtesy of Callaway Gardens
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Cason Jewell Callaway inspects the cabbage crop at one of his experimental farms, circa 1933.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
trp185.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
Cason Callaway pictured with his son Bo Callaway at Cason's Blue Springs Lodge near Hamilton, Georgia, circa 1950.
Courtesy of Troup County Archives, LaGrange, Callaway Gardens Collection,.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Fuller E. Callaway Jr. is pictured working in the lab at Callaway Mills, probably in the 1940s.
Courtesy of Troup County Archives, LaGrange, Callaway Educational Association Collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Mildred Lewis Rutherford taught at the Lucy Cobb Institute in Athens from 1880 to 1928, serving as principal of the school for twenty-two of those years. A prominent member of the United Daughters of the Confederacy and an advocate for the "Lost Cause" interpretation of the Civil War, Rutherford also published a number of books on southern history.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
Mildred Lewis Rutherford, a teacher, historian, writer, and lecturer known primarily for her Confederate memorial activities, published a monthy periodical entitled Miss Rutherford's Scrap Book from 1923 to 1926.
From Miss Rutherford's Scrap Book, vol. 4, April 1923
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
James Blount served as the U.S. representative for the Sixth District of Georgia from 1873 to 1893. In the months following his 1893 retirement, Blount investigated the Hawaiian Revolution of that same year and reported to the U.S. government that most Hawaiians were opposed to annexation by the United States.
Courtesy of Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division, Brady-Handy photograph collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Henry Tift's sawmill, circa 1900. After the success of the sawmill, Tift expanded his business interests by establishing the Tifton Cotton Mill and the Bank of Tifton.
Courtesy of Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library, University of Georgia Libraries, Albertype Co, Photographs.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
A successful businessman and developer, Henry H. Tift founded the south Georgia town of Tifton.
Courtesy of Coastal Plain Experiment Station
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
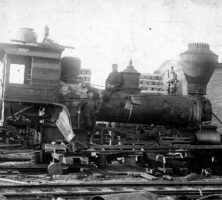
This locomotive, long used at the Tift sawmill, was said to have seen service in the Civil War before it was bought by Henry Tift.
Courtesy of Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library, University of Georgia Libraries, Wesley Thomas Hargrett Collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
The lumberyard at Henry Tift's sawmill at Tifton, around 1900. Tift established his sawmill at the highest ground in the area.
Courtesy of Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library, University of Georgia Libraries, Albertype Co, Photographs.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
The carving on Stone Mountain depicts the Confederate icons Robert E. Lee, Thomas "Stonewall" Jackson, and Jefferson Davis. Commissioned by the president of the United Daughters of the Confederacy, the sculptor Gutzon Borglum began work on the relief in 1915. He was fired in 1925, and Augustus Lukeman completed the carving.
Photograph by Mark Griffin, Wikimedia
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
John Wellborn Root's eight-story Equitable Building in Atlanta, built in the early 1890s for the developer Joel Hurt, was demolished in 1971, just as Georgia's historic preservation movement was getting under way. Its steel-frame construction and monumental presence made it the city's pioneer skyscraper.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Georgia Department of Community Affairs, Historic Preservation Division.
Atlanta businessman Joel Hurt was involved in real estate, insurance, and streetcars. He was responsible for the construction of three major buildings in downtown Atlanta, including the Hurt Building and the Equitable Building.
Courtesy of Atlanta Historical Society
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The Hurt Building, named for Atlanta developer Joel Hurt and completed in 1926, was the seventeenth-largest office building in the world; still standing, it remains a distinctive Atlanta landmark.
Photograph by Ganeshk
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Nellie Peters Black, on the Peters family farm with her daughters. Black was a proponent of the Country Life Movement as well as a crusader for agricultural diversification.
Courtesy of Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library, University of Georgia Libraries, Nellie Peters Black Papers.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
Nellie Peters Black personified the early club woman movement in the South, belonging to numerous civic and social organizations.
Courtesy of Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library, University of Georgia Libraries, Nellie Peters Black Papers.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
Nellie Peters Black served three terms as president of the Georgia Federation of Women's Clubs. She led Georgia women in supporting U.S. president Woodrow Wilson's thrift and conservation campaigns during the Progressive era.
Courtesy of Hargrett Rare Book and Manuscript Library, University of Georgia Libraries, Nellie Peters Black Papers.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
Riding in a car decorated as a float, representatives of the Georgia Young People Suffrage Association participate in a 1920 parade.
Courtesy of Georgia Archives, Vanishing Georgia, #
geo088.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Georgia Archives.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Watson, one of Georgia's most promising politicians of the late nineteenth century, was elected to Congress in 1890 as a Southern Alliance Democrat. Within a year he shocked Georgians by quitting his party, joining the Populists, and founding a newspaper called the People's Party Paper.
Courtesy of Watson-Brown Foundation, Inc.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
In 1892 Georgia politics was shaken by the arrival of the Populist Party. Led by Thomas E. Watson of McDuffie County, this new party mainly appealed to white farmers, many of whom had been impoverished by debt and low cotton prices in the 1880s and 1890s. The Populists also attempted to win the support of Black farmers away from the Republican Party.
Courtesy of Georgia Historical Society.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to Georgia Historical Society.
Watson was narrowly defeated in his 1892 bid for reelection to Congress by his Democratic opponent, as he would be again in 1894. In 1918 he made another bid for Congress but lost to Carl Vinson. In 1920 Watson entered his final political race and achieved his first success in more than two decades when he ran for the U.S. Senate.
Courtesy of the Watson-Brown Foundation, Inc.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
This twelve-foot statue of Thomas Watson was installed in 1932 and moved away from the capitol amid controversy in 2013.
Photograph by Wally Gobetz
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Thomas Watson ran for president in 1904 and 1908 on a platform that vigorously endorsed white supremacy. He never won more than 1 percent of the nationwide vote while running for president.
Photograph by Wikimedia
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Atlantan Henry Grady, a prominent orator and editor of the Atlanta Constitution, heralded the coming of the New South after the end of the Civil War.
Courtesy of Special Collections & Archives, Georgia State University Library, Lane Brothers Commercial Photographers Photographic Collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to Special Collections and Archives at Georgia State University.
Between 1880 and 1886 the Atlanta Constitution became the primary instrument of the Atlanta Ring, a loosely connected group of urban, proindustry Democrats. Henry Grady became the group's leader and dominant political force, helping to arrange the legislature's election of a fellow Ring member, Joseph E. Brown, to the U.S. Senate in 1880.
Courtesy of Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives, and Rare Book Library, Emory University, Henry Woodfin Grady Papers.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. For more information about this resource, contact the Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives, and Rare Book Library at Emory University.
With his New South platform, Henry W. Grady advocated unity and trust between the North and South and helped to spur northern investment in Atlanta industries.
Courtesy of Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives, and Rare Book Library, Emory University, Henry Woodfin Grady Papers.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. For more information about this resource, contact the Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives, and Rare Book Library at Emory University.
Rebecca Latimer Felton, the nation's first female senator, wrote My Memoirs of Georgia Politics after her seventy-fifth birthday. Through speeches and her writings, she helped to effect statewide prohibition and to bring an end to the convict lease system in Georgia.
From History of the Georgia Woman's Christian Temperance Movement, by Mrs. J. J. Ansley
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A writer and tireless campaigner for progressive reforms, especially women's rights and woman suffrage, Rebecca Latimer Felton was the first woman to serve in the U.S. Senate.
From Prominent Women of Georgia, edited by J. B. Nevin
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Rebecca Latimer Felton (seated) was the first woman to be sworn into the U.S. Senate on November 21, 1922, as a replacement for Thomas E. Watson, who died while in office. Her term lasted for twenty-four hours before the inauguration of Walter F. George, who won the special election for the seat.
Courtesy of Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Amanda America Dickson, the daughter of an enslaved woman and her enslaver, became one of the wealthiest Black women in nineteenth-century America when the Georgia Supreme Court upheld her claim to her father's contested will. Dickson inherited his estate in Hancock County upon his death in 1885.
Courtesy of Georgia Historical Society.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to Georgia Historical Society.
Lucy Craft Laney’s portrait, pictured, was the first portrait of an African American woman to be displayed in the Georgia state capitol. It was selected by Governor Jimmy Carter in 1974. Laney was also inducted into the Georgia Women of Achievement in 1992.
Courtesy of Georgia Capitol Museum, University of Georgia Libraries, Capitol Art Collection (Capitol Museum Collection), # 1992.23.0050.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Asa Griggs Candler, founder of the Coca-Cola Company, was also a banker and real estate developer and was noted for his philanthropy. His best-known philanthropy was in the form of a personal check for $1 million, donated to defray the costs of establishing Emory University in Atlanta as a Southern Methodist institution.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. For more information about this resource, contact the Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives, and Rare Book Library at Emory University.
In 1916 Candler was elected as a reform mayor to sort out Atlanta's chaotic fiscal situation. At this point he handed over control of most of his business enterprises, including The Coca-Cola Company, to his children.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. For more information about this resource, contact the Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives, and Rare Book Library at Emory University.
One of the most influential African American leaders in late-nineteenth-century Georgia, Henry McNeal Turner was a pioneering church organizer and missionary for the African Methodist Episcopal Church (A.M.E.) in Georgia.
Courtesy of Georgia Historical Society.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to Georgia Historical Society.