The New Georgia Encyclopedia is supported by funding from A More Perfect Union, a special initiative of the National Endowment for the Humanities.
St. Catherines Island, located in Liberty County, is one of the barrier islands lining the coast of Georgia. The privately owned island, a National Historic Landmark, is about ten miles long and approximately one to three miles wide. From the 1590s to the 1680s a Spanish mission, Santa Catalina de Guale, was located on the island (at that time part of the Spanish colony La Florida).
Photograph by Jason D. Williams
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Hernando de Soto was a Spanish-born explorer and conqueror who landed in present-day Tampa Bay, Florida, in 1539 and came to the Georgia area in 1540. Chroniclers of the expedition described the Coosa River valley in glowing terms.
Courtesy of Georgia Info, Digital Library of Georgia.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Digital Library of Georgia.
An 1866 tobacco label depicts Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto and his crew being welcomed ashore by Native Americans. De Soto entered Georgia twice in 1540, encountering the Altamaha, Capachequi, Coosa, Ichisi, Ocute, Patofa, Toa, and Ulibahali chiefdoms during his travels in the area.
Courtesy of Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A watercolor by Herbert Rudeen illustrates Tristan de Luna's historic landing at Pensacola Bay in August 1559. De Luna's failed plan to establish a Spanish presence along the lower Atlantic coast, the Gulf Coast, and the interior of the Southeast included the colonization of Ochuse (Florida), Coosa (Georgia), and Santa Elena (South Carolina).
Courtesy of Pensacola Historical Society
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A drawing from Lambert A. Wilmer's Life, Travels and Adventures of Ferdinand de Soto, Discoverer of the Mississippi (1859) depicts Hernando de Soto and his men crossing the Chattahoochee River. The accidental introduction of European diseases by explorers destroyed many of the civilizations along the river's banks.
Courtesy of Florida State Archives, Photographic Collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A 1791 engraving depicts Pedro Menendez de Aviles at about age fifty. Menendez de Aviles founded St. Augustine, Florida, the oldest European settlement in North America, in 1565, just before he explored the Georgia coastline.
From The Spanish Settlements within the Present Limits of the United States: Florida, 1562-1574, by W. Lowery
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Modern-day steps lead to the summit of one of the Indian mounds at the Etowah site.
Courtesy of Georgia Department of Natural Resources, Georgia State Parks.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Georgia Department of Natural Resources.
The Creek Indians meet with James Oglethorpe. By the time Oglethorpe and his Georgia colonists arrived in 1733, relations between the Creeks and the English were already well established and centered mainly on trade.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
Charles Bird King's portrait of William McIntosh (ca. 1825). In 1825 McIntosh negotiated and signed the Treaty of Indian Springs, signing away all Creek lands in Georgia and thereby defying most of the reforms that he had encouraged and the laws that he had helped write.
Image from Archives and Rare Books Library, University of Cincinnati Libraries, McKenney and Hall: History of the Indian Tribes Collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
This copy of a Creek "hieroglyphick painting" was made in the 1770s by Bernard Romans. Romans was a British surveyor and engineer who worked in Florida during the 1770s. He made many notes on the Creeks.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
A civil war between the United States and the Creeks erupted in 1813. In a final battle in March 1814 at Horseshoe Bend in Alabama, General Andrew Jackson (left) directed the killing of 800 Creeks. The Red Stick War officially ended in August 1814 with the Treaty of Fort Jackson.
Image from the New York Public Library Digital Collections, The Miriam and Ira D. Wallach Division of Art, Prints and Photographs: Picture Collection.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A brief conflict between the United States and Creeks in 1836 ended with U.S. troops, assisted by Georgia and Alabama militia, rounding up Creeks and forcibly sending them to Indian Territory (Oklahoma).
Reprinted by permission of The Granger Collection, New York
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
This watercolor portrait of "General" Kipahalgwa of the Yuchi Indians was painted by the German artist Philip Georg Friedrich von Reck around 1734. Kipahalgwa is depicted wearing an English-style shirt, leggings, and shoes.
Illustration by Philip Georg Friedrich von Reck
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Painter Philip Georg Friedrich von Reck identifies this couple as Senkaitschi, a Yuchi king, and his queen. The queen's blanket, which the artist describes as "a British blanket from Charles Town," offers evidence of trade with Europeans.
Illustration by Philip Georg Friedrich von Reck
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
This illustration shows the Yuchi Indians of Georgia with popular adornments and accessories including: a) ring and pearl worn by some in the nose, b) corals, c) arrows and lines burned into the chest, and d) ladle made from a buffalo horn.
Illustrations by Philip Georg Friedrich von Reck
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Georgia's Yuchi Indians were one of many refugee tribes in the area during the eighteenth century. They eventually joined with the Lower Creek Indians. Here the Yuchi Indians are depicted in a war dance.
Illustration by Philip Georg Friedrich von Reck
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Yuchi Indians, depicted in traditional hunting clothing, also carry items acquired through trade with the English, notably the central figure's blanket and rifle.
Illustration by Philip Georg Friedrich von Reck
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
A view of the immediate area where the Macon Trading Post was located.
Photograph by Dsdugan / CC0
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
Archaeologists excavated a prehistoric Indian village in Rucker's Bottom near the Savannah River about 500 years after the civilization's height.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource should be submitted to the Hargrett Manuscript and Rare Book Library at the University of Georgia.
A path leading to two of the mounds at the Etowah Indian Mounds Historic Site. Located in Bartow County, the site is home to the second-largest Indian mound in North America, rises to a height of slightly more than 60 feet.
Photograph from Sharon Meier
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.
The chiefdom of Ichisi was located between modern Macon and Perry on the Ocmulgee River. The capital town was probably located at the present-day Lamar archaeological site, a part of Ocmulgee Mounds National Historical Park.
Courtesy of Georgia Department of Economic Development.
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. Requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource may need to be submitted to the Georgia Department of Economic Development.
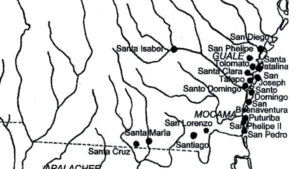
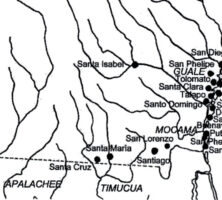
Courtesy of John Worth
The New Georgia Encyclopedia does not hold the copyright for this media resource and can neither grant nor deny permission to republish or reproduce the image online or in print. All requests for permission to publish or reproduce the resource must be submitted to the rights holder.